Problem:
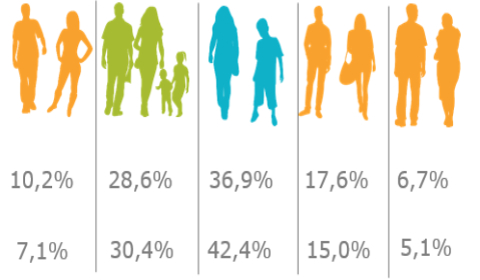
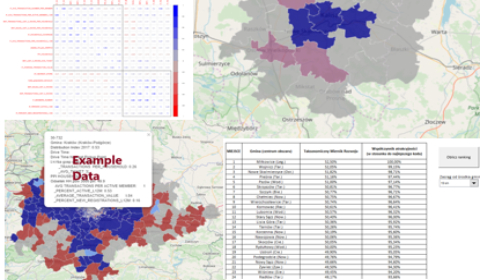
One of the retailers, in order to diversify its offer and communication, wanted to distinguish business-relevant segments in a database of almost 4 million registered consumers.
Rozwiązanie:
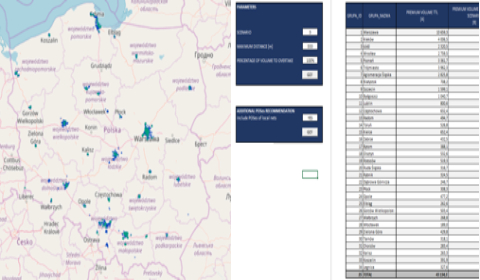
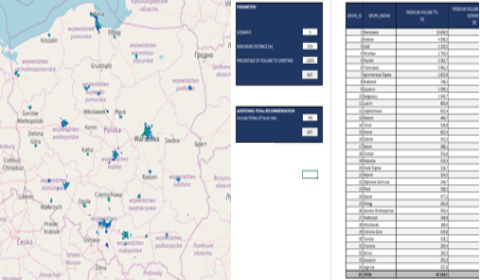
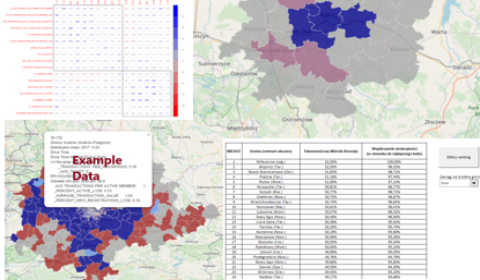
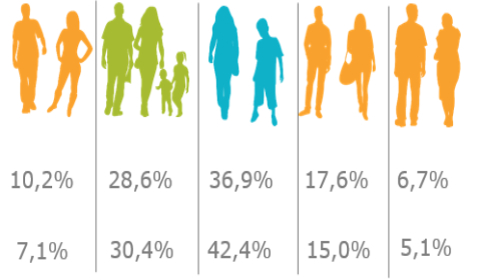
Using machine learning methods, 5 customer segments were identified based on nearly 100 variables. These segments were characterised and described for marketing purposes. Each customer in the database was assigned a segment with the possibility of periodical automatic refreshing.
Effects:
- Automation of the cyclic segmentation refreshing allows to save time for marketing and analytic tasks by approx. 40%
- Adjustment of the offer and language to the customer segment
- Tracking customer migration between segments in time
- Possibility to assess the increase in effectiveness of marketing activities addressed to a specific segment
Data sources:
- Sales data
- Product data
- Promotion calendar